
Home | About Us | JCPS Home | EHS Science Video
- Chemistry Topics: 1) Matter and Measurement, 2) Atoms, Molecules, and Ions, 3) Stoichiometry, 4) Aqueous Solutions, 5) Thermochemistry, 6) Periodic Properties, 7) Solids, Liquids, and Gases, 8) Chemical Bonding, 9) Molecular Geometry, 10) Properties of Solutions, 11) Chemical Kinetics, 12) Chemical Equilibrium, 13) Acid-Base Chemistry, 14) Thermodynamics, 15) Electrochemistry, 16) Nuclear Chemistry
Lead
by Juliet McKinney
The history of lead is very difficult to know completely because it was used in so many different countries during the middle ages. This is why we do not know for sure who discovered the element first. There is not a tangible date to know when the element was used first, because it was mentioned in the bible, and there are artifacts dating back to 6400 BC.
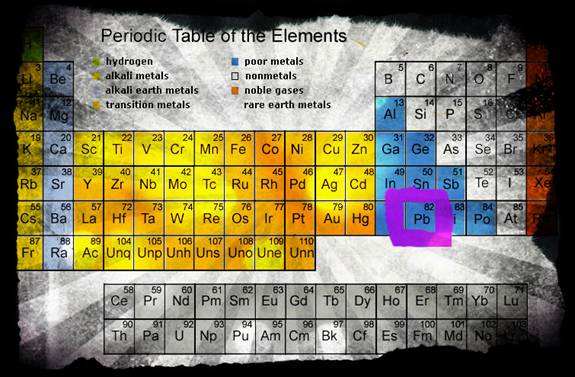
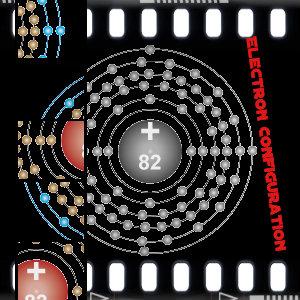
With the atomic number of 82 you can find the energy saving element Pb, otherwise known as lead. With a high density, and a melting point of 326 degrease Celsius, lead is corrosion resistant. Lead also has a high specific weight. It is able to withstand extreme conditions for an extended amount of time, and is long lasting.
Lead’s Electro negativity ranges from about 1.55 go around 2.33. The reason there is a range is because there have been many changes though out the years on Electro negativity charts. The ionization energies of lead are:
- 715.6
- 1450.5
- 3081.5
- 4083
- 6640
Photographs:


Works Cited:
"properties of lead atoms." Webelements. Webelements, 1 Jan. 1993. Web. 1 Nov. 2012. <www.webelements.com>lead>.
"Lead Physical properties." Rohr +Stolberg. Calder Group, n.d. Web. 1 Nov. 2012. <www.roehr-stolberg.de/.../lead-physical>