
Home | About Us | JCPS Home | EHS Science Video
- Chemistry Topics: 1) Matter and Measurement, 2) Atoms, Molecules, and Ions, 3) Stoichiometry, 4) Aqueous Solutions, 5) Thermochemistry, 6) Periodic Properties, 7) Solids, Liquids, and Gases, 8) Chemical Bonding, 9) Molecular Geometry, 10) Properties of Solutions, 11) Chemical Kinetics, 12) Chemical Equilibrium, 13) Acid-Base Chemistry, 14) Thermodynamics, 15) Electrochemistry, 16) Nuclear Chemistry
Caesium
Cesium
By: Elizma Lee

3rd period chemistry: Mr. Steineker, Eastern High School.
Caesium; the name comes from the Latin 'caesius', meaning sky blue, and derived from its flame color.

History:
 In 1860 two German Scientist, Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff discovered Caesium in the mineral water from Dürkheim, Germany. Caesium was the first element to be discovered spectroscopic-ally, only one year after the invention of the spectroscope by Bunsen and Kirchhoff.
In 1860 two German Scientist, Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff discovered Caesium in the mineral water from Dürkheim, Germany. Caesium was the first element to be discovered spectroscopic-ally, only one year after the invention of the spectroscope by Bunsen and Kirchhoff.

Physical:
Caesium or Cesium is a solid chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28 °C, 82 °F and the density of 1.873. It darkens in the presence of trace amounts of oxygen. The atomic radius is 3.430. The abundance varies to 1 to 3 parts per million of the earth in the middle.

Chemical:
When Caesium reacts with water it creates an explosion because the metal is extremely reactive and pyrophoric. When igniting in air, it reacts explosively even at low temperatures, more than other members of the first group of the periodic table. The reaction with solid water occurs at temperatures as low as −116 °C (−177 °F). Electro negativity is 0.790 (Pauling Scale) & Ionization energy: 1st- 375.704, 2nd- 2234.352. Caesium reacts well with acids, the halogens; sulfur, and phosphorus.
BOHR MODEL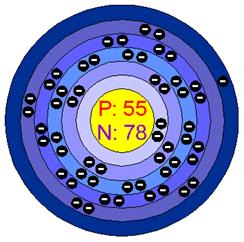
Caesium is located in the first group and fifth row.
Extra information:
Caesium has a limited number of uses. One is as a getter in bulbs and evacuated tubes. The bulb must be as free from gases as possible to work properly. Small amounts of cesium react with any air left in the bulb. It converts the gas into a solid cesium compound. Caesium is also used in photoelectric cells, devices for changing sunlight into electrical energy. Another important use of cesium today is in an atomic clock. An atomic clock is the most precise method now available for measuring time
Sources:
"Cesium, Chemical Element - Overview, Discovery and naming, Physical properties, Chemical properties, Occurrence in nature, Isotopes." Chemistry: Foundations and Applications. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 Nov. 2012. <http://www.chemistryexplained.com/elements/A-C/Cesium.html#b>.
" Periodic Table of Elements and Chemistry. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 Nov. 2012. <http://www.chemicool.com/elements/cesium
“cesium Facts, information, pictures | Encyclopedia.com articles about cesium." Encyclopedia.com | Free Online Encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 Nov. 2012. <http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/cesium.aspx>.